Unlocking Automotive Safety: How LLM-Augmented Tools Are Transforming Hazard and Risk Assessments
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive safety engineering, the Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) process is crucial. This procedure demands extensive engineering expertise to meet the requirements of safety standards like ISO 21448 (SOTIF) and ISO 26262 (Functional Safety). The field of generative AI, especially large language models (LLMs), promises to revolutionize how we approach HARA, particularly in the light of more complex operational design domains, faster release cycles, and the shortage of skilled safety personnel. In this article, we present LASAR (LLM-Augmented Situation Space Analysis for Risk Assessment), an approach that demonstrates the potential of LLM-augmented tools to improve HARA for automotive systems. LASAR integrates human-AI collaboration to enhance HARA, ensuring efficiency without compromising on reliability.
The Challenge of HARA in Automotive Safety Engineering
HARA is a cornerstone of safety engineering, essential for identifying and mitigating risks in automotive systems. The process demands a deep understanding of the system, its environment, and compliance with stringent standards like ISO 26262. Historically, this has required the concerted efforts of experienced safety engineers, making it both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Conducting a HARA in the automotive domain involves defining the assessment’s scope, including identifying the vehicle systems, components, or functionalities that will be analyzed. Next, potential hazards are identified. Once hazards are identified, the risks associated with each are evaluated by assessing their exposure value (likelihood of occurrence), the potential severity of harm, and the controllability of the hazardous event. The next step is to formulate safety goals. These are functional objectives or top-level safety requirements, and they must be suitable for preventing or mitigating hazardous events.
The Intersection of LLM and Automotive Safety Engineering
Generative AI, particularly LLMs like ChatGPT, offers new possibilities for automating complex and creative tasks. Large language models are designed to create context-specific data. LLMs can process multiple inputs, while effectively understanding and integrating various context information. This allows us to combine the inputs into a specific scenario in fine detail. The complexity involved in understanding and synthesizing diverse inputs is a highly creative task that requires significant expertise. Conducting a HARA requires creative evaluation of various scenarios and the risks associated with them. Thus, LLMs have the ability to assist in this task. Although language models have not yet reached the reliability required to independently oversee safety-critical domains such as automotive engineering, this study presents a promising hybrid approach. By integrating human-AI collaboration, we aim to significantly improve the Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment (HARA) process.
More About LLMs and Gen AI
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Chat with your own data
- Prompt Engineering: How to communicate with large language models
- Hallucinations: How hallucinations reduce the reliability of LLM applications
Key Challenges:
- Complex and Creative Task: Today, HARA and many other safety engineering processes require high expertise to create high-quality artifacts and fulfill standards and norms
- Complex Environment: With increased automation, the environment has a greater impact on safety analysis. Currently, there is no tool support to analyze the environment efficiently and effectively and identify those elements and situations that are relevant for risk assessment and other safety engineering processes
Our Solution: Introducing LASAR – A Human-AI Cooperative Tool
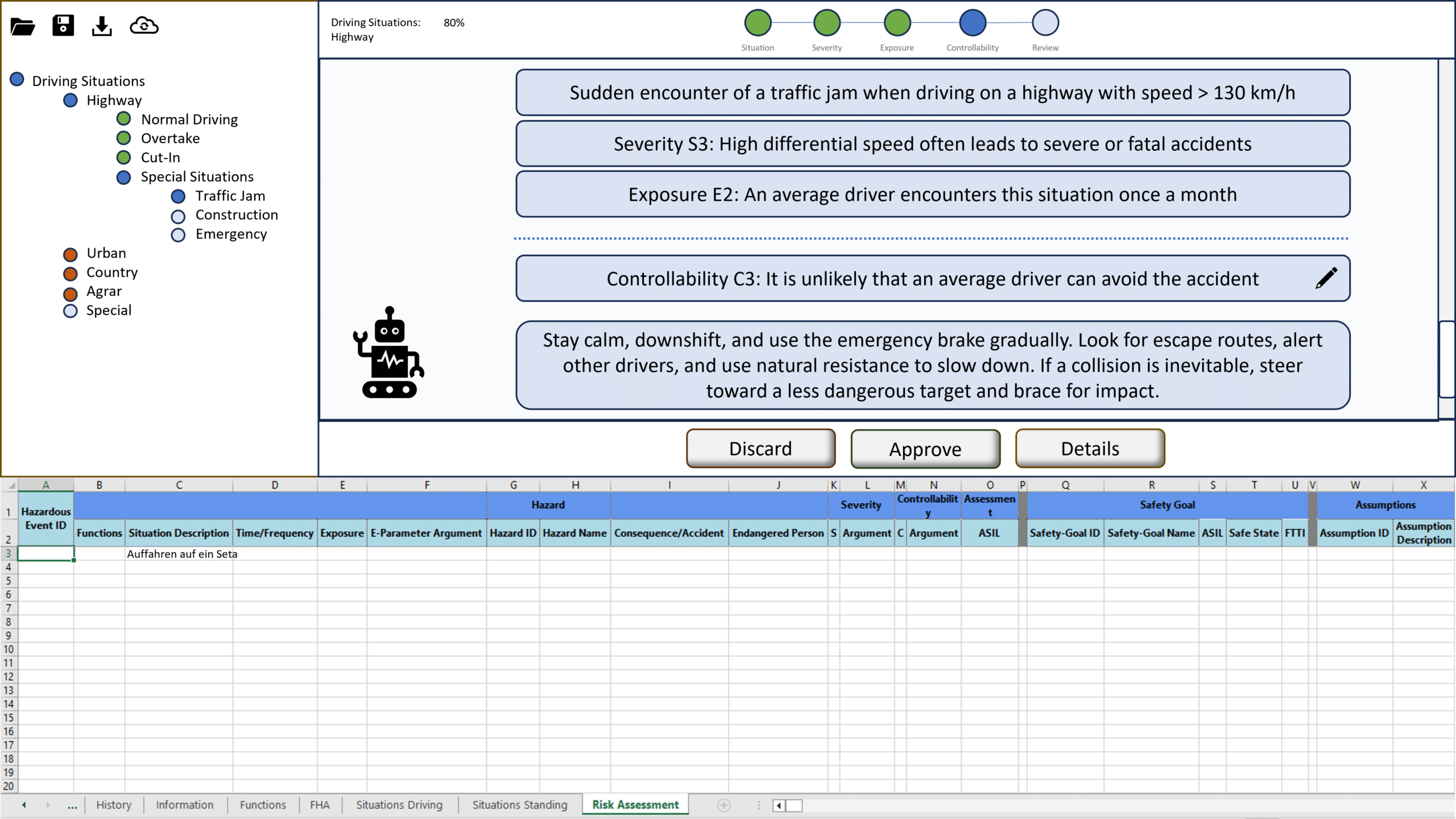
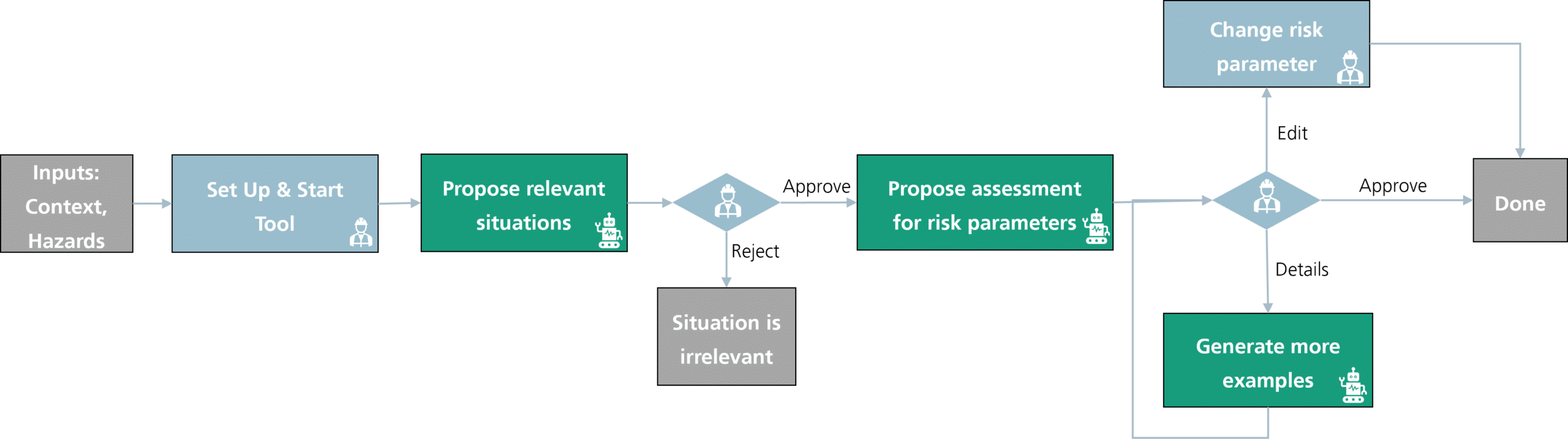
LASAR (LLM-Augmented Situation Space Analysis for Risk) is a tool designed to assist safety engineers in conducting HARA. LASAR employs LLMs to provide preliminary assessments, arguments, and examples, which human engineers can then review, modify, or approve. The results are automatically inserted into the HARA table, saving the engineers time. The GUI mockup shows the assessment of severity, exposure, controllability values, and a mitigation strategy for a given hazard in a specific situation. This collaboration between LLM and the engineer aims to increase efficiency while ensuring the assessments‘ accuracy and compliance with industry standards.
Key Features of LASAR:
- Interactive Workflow: Engineers actively engage with the tool to filter scenarios from a situation catalog, ensuring that the LLM does not exclude any important or relevant situations. This interaction is crucial because it allows engineers to verify and refine the initial categorizations made by the LLM based on the preliminary Operational Design Domain (ODD) and system context. Additionally, this process saves time, as engineers only need to go through the initial categorization into relevant and irrelevant scenarios suggested by the LLM, streamlining the initial stages of hazard analysis and focusing efforts on high-priority issues.
- Step-by-Step Guidance: The tool provides detailed assessments of risk parameters such as severity, exposure, and controllability with reasoning and real-world examples. This detailed explanation helps engineers visualize each scenario more clearly, allowing for a deeper understanding of the potential impacts and mechanisms of each hazard in each situation. Additionally, by presenting various perspectives through the reasoning, the tool helps engineers consider alternative viewpoints on the situation, which can lead to more robust decision-making and enhanced safety measures.
- Human Oversight: Engineers review and validate the tool’s suggestions, ensuring that the final HARA is accurate and comprehensive.
The Benefits: Why Your Company Should Consider This Approach
- Efficiency Gains: The tool’s preliminary assessments provide a valuable starting point, making the risk assessment process more efficient.
- Improved Quality: Engineers reported increased confidence in the HARA’s quality due to the tool’s detailed reasoning and examples.
- Human-AI Synergy: The collaborative approach ensures that the final assessments were both high-quality and compliant with ISO 26262.
- Automatic Generation of the HARA Table: The tool provides an output in the form of a HARA table to be used and integrated into existing templates.
Partner with Us for Enhanced ADS Safety
As the automated driving industry continues to grow, ensuring the safety of ADS across diverse operational environments is more critical than ever. Our GenAI-human collaboration tool LASAR offers support to analyze the environment and to increase the effectiveness of safety engineering processes.
We invite companies developing autonomous driving systems to partner with us in integrating this innovative approach into their safety engineering processes and existing toolchains. We would like to provide you with additional information and a demonstration of our GenAI-human co-engineering approach. Together, we can help you:
- Enhance your safety engineering processes with Generative AI for your ADS and ADAS development.
- Analyze the environment and identify those situations and elements that are relevant to your process to increase the effectiveness and reduce complexity.
Conclusion
The integration of LLM-augmented tools like LASAR represents a significant step forward in automotive safety engineering. By combining the strengths of AI and human expertise, these tools can make the HARA process more efficient, accurate, and comprehensive. As technology matures, we can expect even greater advancements, paving the way for safer and more reliable automotive systems. LASAR and similar tools offer a glimpse into the future of risk assessment, where human-AI collaboration ensures the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
References
[1] D. Hillen, C. Helten, and J. Reich „Towards LLM-augmented Situation Space Analysis for the Hazard and Risk Assessment of Automotive Systems“, GRANITE – EJEA: Europe meets Japan: Intercultural Workshop on Data Sovereignty and Generative AI: Applications, Design, Social, Ethical and Technological Impact, 2024

