Public services in the digital age
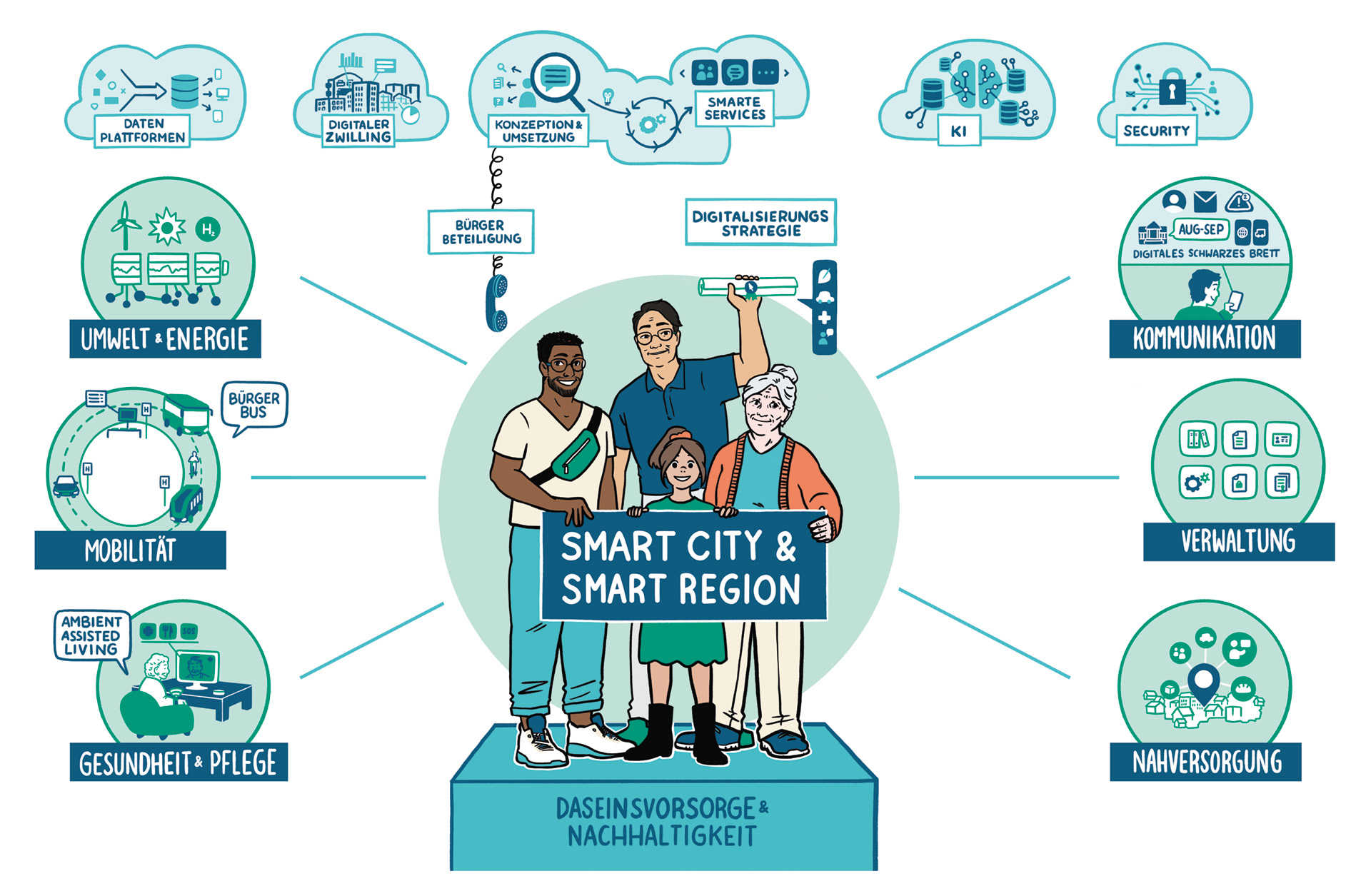
Nowadays, municipalities are active in many fields of activity: They provide administrative services and ensure the supply of the population. Accordingly, public services cover a wide range of services. They include areas such as local supply, waste disposal, and (digital) infrastructure as well as the provision of educational offerings, energy, mobility, or cultural offerings. Municipal players now have a great deal of scope for shaping the provision of public services. These can increasingly be provided digitally – and make a tangible contribution to improving the quality of life.
Recognizing the potential of digitalization
Demands on the supply with goods and services do not only change over time. The spatial context also influences the priorities of municipal players. In many rural areas, for example, the focus is primarily on ensuring areawide services. Here, digitalization offers effective tools for planning and implementing public services. In larger cities and metropolitan areas, on the other hand, the requirements for intelligently networked systems, e.g., in the areas of mobility or energy, are increasing all the time. The topic of Smart Cities has become a comprehensive field of activity. However, as the complexity of the tasks increases, so do the demands on the associated planning processes. Such new areas of responsibility for municipalities and the municipal economy do, among other things, lead to the need to develop suitable competencies in the workforce and, in some cases, even integrate new types of professions. At the same time, aspects such as ecological, economic, and social sustainability, the resilience of technical and organizational systems, and equality of living conditions must not be overlooked.
Making digital public services fit for the future
Innovative software and networked systems represent only partial aspects of municipal digitalization. New potentials are also opening up, e.g., with regard to the participation of citizens and the employees of municipal enterprises. Through its extensive research activities, Fraunhofer IESE covers the entire breadth of the topic of digital public services – from the conception and implementation of smart solutions to user participation and target-group-specific knowledge transfer. We support municipalities in making their public services digital and future-proof.